Dr. Arnold - Pelvic Floor Training - Pelvi Touch
Already in 1948, Arnold Kegel wrote about pelvic floor training to counteract incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse and fecal incontinence. The training scheme he developed is what we know today as Kegel exercises. Arnold Kegel naturally inspires the creation of the Dr. Arnold chair.
To read about pelvic floor training specifically for men click here.
Female urinary incontinence is a common problem. 12.4% of the female population in the world is affected by urinary incontinence. Of these women, 54.3% of them say that the problems affect their quality of life. Men also suffer from this type of problem. Unfortunately, this is something that we don’t like to talk about and few know that there are actually treatments that can make a difference completely without surgery and without pain, without the risk of burns, scarring or swelling.
There is a complex variety of changes in the pelvic floor system that occur naturally with age or after childbirth. In these cases, the pelvic floor muscles (PFM) do not provide sufficient support for the pelvic organs and continence control. This leads to PFM dysfunctions causing urinary incontinence. Strong pelvic floor muscles provide control over the bladder and bowel.
-Don’t let incontinence problems affect your everyday life when a solution is so close at hand. Book a free consultation or directly book a first visit where we do both a consultation, health declaration and investigation as well as an initial treatment. Warm welcome!
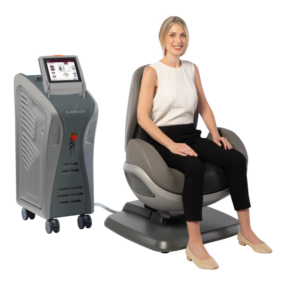
During a treatment, you sit FULLY CLOTHED in the chair and can e.g. read a book.
Pelvic floor training treats urinary incontinence, both stress incontinence and urge incontinence. It is suitable for pelvic floor rehabilitation after childbirth and for reduced intimate satisfaction. Pelvic floor training can in many cases also help you who suffer from chronic pelvic pain syndromes such as vestibulitis where Myofascial physical therapy (MPT) treatment is recommended. Dr. Arnold is suitable for both women and men.
Dr. ARNOLD uses a unique magnetic and selective stimulation sequence, TOP FMS, which interacts with neuromuscular tissues by inducing homogeneous intense muscle contractions (greater than any individual can achieve naturally) without pain or discomfort. Manufactured by the medical technology Italian company DEKA.
Dr. ARNOLD has a preventive effect on many areas of women’s and men’s intimate health:
• Gynaecological: preventive treatment of genital prolapse (prolapse, weakening of the vaginal wall).
• Urological: preventive treatment of urinary incontinence, by improving urethral support and the closing mechanism, especially during exertion.
• Colorectal: prevention-restoration of anorectal function (rectal function).
• Sexual: positive impact on sex life, by strengthening the perineal muscles.
We recommend a starting regimen of 8 treatments, usually twice a week.
The vast majority notice a big difference or get rid of the problem completely after a course.
To maintain the achieved results, maintenance sessions are recommended.
First visit
On your first visit, you will fill in a health declaration and we will go over your complaints. In some cases, we do some quick tests to get a clearer picture of your particular problem. After that, you get to settle into the Dr. Arnold chair. You sit fully clothed during the treatment. After the treatment, you can continue your life as usual. No preparation is needed either. For your further treatments, the visit only takes 30 minutes each time. You come twice a week with at least one, preferably 2 days in between. A basic course consists of 8 treatments.
We do not treat:
-people with a pacemaker / other metal object in the body (copper spiral or metal uterine ring), electronic implants, defibrillators, neurostimulators, drug pumps implanted at the treatment site.
-If you have a hip prosthesis, it must be made of titanium, if it is made of other metal, we will not treat you.
– if you have malignant swelling.
– if you have epilepsy.
– if you have recently had surgery.
-immediately after delivery.
– in case of unhealed birth injuries.
INFO IN CASE OF BIRTH INJURIES
– If you have a birth injury, you must let it heal before any treatment.
–Are you in pain after giving birth but the doctor says everything looks fine? Then think that you are right and they are wrong. It is NOT normal to have pain, leak urine, have difficulty going to the toilet, etc. after giving birth. The first few weeks yes, but not after that.If you do not get the help you need, turn to another reception. There are groups that can help you find the right help and support you with your rehabilitation. Many times you are advised to work with pinch exercises even though they cause you more pain. Instead, it could be that you have an overstretched pelvic floor and that what you need to do is learn to relax, just the opposite of the advice given. If you suspect that you have a birth injury even though the healthcare claims otherwise, we recommend that you contact others who have experienced the same thing. A person/group that we are happy to refer to is Frida Trönnberg på Helt underliv och “Allt ser fint ut”.
TOP FMS: modulated stimulation on muscle tissue. The special and unique TOP Flat Magnetic Stimulation technology – designed exclusively by DEKA R&D – ensures homogeneous and even intensity distribution without peaks over a sufficiently wide area, which prevents pain experiences and discomfort in the patient.
Learn more about incontinence
Urinary incontinence is often divided into a few different types depending on when incontinence occurs. The most common types of urinary incontinence are presented below:
● Stress incontinence: This is the most common type of urinary incontinence and means that it is difficult to keep tight because the pressure becomes too high in the stomach and bladder. Then a little urine may leak if, for example, you sneeze, cough or do anything else that increases the pressure. This urine leakage can happen without you feel the need to urinate. It is more common for women to suffer from this type of stress incontinence.
● Urge incontinence: This type of incontinence means that you suddenly feel the need to pee and then have difficulty holding in. With this incontinence is it is common to need to urinate often. It is more common for women to be affected this type of urinary incontinence.
● Mixed incontinence: Mixed incontinence is a mixture of stress incontinence and urge incontinence. This incontinence means in other words, that you both have difficulty keeping tight when you exert yourself and that
you suddenly feel the need to pee and have difficulty holding on. It is more common to women suffer from this type of urinary incontinence.
● Overflow incontinence: The fourth of the different types of urinary incontinence is overflow incontinence which means difficulty emptying the bladder completely,
which causes the bladder to stretch instead. When the bladder becomes overfilled, squeeze the urine out of the bladder through the prostate gland and the urine often leaks in small amounts splashes. If this type of urinary incontinence is not detected in time, it can cause damage to the kidneys and bladder. It is more common for men to be affected of this type of urinary incontinence.
● Functional incontinence: Functional incontinence means that a mental or physical impairment causes involuntary urination. For example, it can be about
an individual with arthritis who has trouble removing his pants in time for urination, which leads to involuntary urination.
There are several possible causes of urinary incontinence and it can occur in conjunction with different stages in life. In general, urinary incontinence is considered to occur due to a disturbance of the function of the lower urinary tract. The lower urinary tract includes the bladder with its detrusor muscle, bladder neck, internal sphincter and urethra. In men also includes the prostate and seminal vesicles. In addition, the pelvic floor muscles have a central function where the external striated and volitionally controlled sphincter is located and it is, among other things, common for urinary incontinence to arise due to a weak pelvic floor muscles. Urinary incontinence can also be caused by changes in
urethra as in benign prostatic hyperplasia which often affects men of increasing age as well asof changes in the bladder. Urinary incontinence also occurs during pregnancy due to the pressure of the fetus on the bladder and after childbirth before the muscle strength in the pelvic floor recovered. In addition, obesity or bladder infections can contribute urinary incontinence. Also neurological impact that can occur in dementia,
spina bifida or spinal cord injuries can lead to difficulties in interpreting the body’s signals such as urge to urinate and/or difficulty emptying the bladder and thus cause
urinary incontinence.
How can incontinence be treated?
Depending on what caused the incontinence problem, there are different options:
In some cases, simple lifestyle changes can help reduce incontinence. This may mean avoiding smoking, caffeine and alcohol, exercising the pelvic floor muscles and avoiding heavy lifting. For some, even weight loss can reduce the problems as abdominal obesity results in a greater load on the pelvic floor with negative effects on the ability of the bladder and urethra to keep tight.
Estrogen is a hormone primarily associated with the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues. It also plays a role in maintaining the health of the urinary tract, including the bladder and urethra. Estrogen can help reduce or prevent incontinence in women by improving the strength and tone of the muscles that control urine flow. In women, the bladder and urethra are supported by a network of muscles and connective tissue called the pelvic floor. These muscles can be weakened or damaged due to pregnancy, childbirth, aging or other factors, leading to incontinence. Estrogen can help maintain the health and function of these muscles, making them stronger and better at controlling urine flow. Estrogen can also help reduce inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract, which can contribute to incontinence. By maintaining a healthy estrogen balance in the body, women can reduce the risk of developing incontinence or improve their symptoms if they already have the condition.
As women age, their bodies naturally produce less estrogen, which can lead to weakening of the pelvic muscles and tissues and can result in urinary incontinence. Estrogen therapy, which involves the use of estrogen supplements, can help reverse some of these changes and reduce the symptoms of incontinence. Estrogen therapy can help strengthen the muscles and tissues in the pelvic area, including the muscles that control urination, by promoting the growth of new cells and improving blood flow to the area. This can help improve bladder control and reduce the frequency and severity of incontinence episodes. However, it is important to note that estrogen therapy is not suitable for everyone and that there are risks associated with its use, including an increased risk of blood clots, stroke and certain types of cancer. Women should discuss the risks and benefits of estrogen therapy with their healthcare provider before deciding whether it is right for them.
Estrogen treatment for incontinence in women is done in several different ways, including:
Oral estrogen: This means taking estrogen supplements in tablet form. Oral estrogen can be effective in treating incontinence, but it can also increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Vaginal estrogen: This means that estrogen supplements are inserted into the vagina in the form of creams, tablets or rings. Vaginal estrogen is often preferred over oral estrogen for the treatment of incontinence because it is more local and has fewer systemic effects. Vaginal estrogen can help improve the health of the tissues in the vagina and the urethra, which can help reduce incontinence symptoms.
Transdermal estrogen: This involves applying estrogen patches to the skin, which deliver a steady stream of estrogen into the bloodstream. Transdermal estrogen can be an effective alternative to oral estrogen, but it can also increase the risk of blood clots and stroke. Women should also be monitored regularly for any side effects or complications associated with estrogen therapy.
Estrogen therapy can be an effective treatment for incontinence in women, but there are also potential risks and benefits to consider. Here are some of the pros and cons of estrogen therapy for incontinence:
Benefits: Improved bladder control. Estrogen therapy can help strengthen the muscles and tissues in the pelvic area, which can improve bladder control and reduce the frequency and severity of incontinence episodes. Improved vaginal health. Estrogen therapy can also help improve the health of the tissues in the vagina and urethra, which can reduce symptoms such as dryness, itching and pain during intercourse. Reduced risk of urinary tract infections: Estrogen therapy can also help reduce the risk of urinary tract infections, which can be a common complication of incontinence.
Cons: Increased risk of blood clots: Estrogen therapy can increase the risk of blood clots, which can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Women who have a history of blood clots or have an increased risk of blood clots may not be good candidates for estrogen therapy. Increased risk of certain types of cancer. Estrogen therapy has been associated with an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including breast cancer and ovarian cancer. Women should discuss their individual risk factors with their healthcare provider before starting estrogen therapy. Other potential side effects. Estrogen therapy can also cause other side effects, including headache, nausea, breast tenderness and vaginal bleeding.
Overall, estrogen therapy can be an effective treatment option for incontinence in women, but it is important to weigh the potential risks and benefits before starting treatment.
A pessary is a small ring or membrane that is placed in the vagina to support the urethra and prevent urine leakage during straining. This can be effective for women with stress incontinence.
In cases where, for example, a urinary tract infection may be the underlying problem, you do a simple test and get an answer immediately. If it is a urinary tract infection, you will be prescribed antibiotics.
There are medications that reduce bladder overactivity or alpha blockers that help reduce pressure on the urethra. It may include anticholinergics to reduce bladder overactivity or estrogen therapy to strengthen the tissues of the urethra.
For some, especially men, using a urinary catheter can be a solution, especially if they have difficulty emptying the bladder completely on their own.
Surgery can be an effective option for treating incontinence, especially for those who have severe symptoms that do not respond to non-surgical treatments, and should always be considered and tried first. The type of surgery recommended depends on the underlying cause of the incontinence.
Here are some common surgical procedures for treating incontinence.
Sling Procedures: A sling is a small strip of synthetic mesh that is inserted through small incisions in the vagina and placed under the urethra. The loop helps support the urethra and prevent urine leakage. There are different types of sling procedures, including tension-free vaginal tape (TVT) and transobturator tape (TOT). TVT surgery is the most common type of surgery done for incontinence.
Bladder neck suspension: This procedure involves using sutures to attach the bladder neck to the pelvic bones to provide support for the bladder and urethra. This can help reduce the symptoms of stress incontinence.
Artificial Urinary Sphincter: This is a device implanted around the urethra to help control the flow of urine. The device has a small pump that is placed in the scrotum (for men) or the labia (for women) and can be manually controlled to open or close the sphincter.
Filler injection: A filler, e.g. collagen or silicone, can be injected into the urethral sphincter to increase its thickness and provide better control over urine flow.
TVT surgery is a commonly performed procedure to treat stress urinary incontinence in women, and like all surgical procedures, it has both pros and cons.
Advantages: High success rate. TVT surgery has been shown to be highly successful in the treatment of
stress urinary incontinence, with up to 85-90% of women experiencing a significant
improvement of symptoms. Minimally invasive: TVT surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that can usually be performed on an outpatient basis with a short recovery time. Low complication rates: Complications associated with TVT surgery are relatively uncommon and usually less serious, such as bleeding, pain, or infection.
Cons: Risk of mesh-related complications: There have been reports of complications associated with the use of synthetic mesh in TVT surgery, e.g. erosion of the mesh, pain and infection. Although these complications are rare, they can be serious and require additional treatment. Limited long-term data: Although TVT surgery has been used for over 20 years, there are limited long-term data on its safety and effectiveness beyond 10 years. Risk of overcorrection or undercorrection: TVT surgery can lead to overcorrection or undercorrection of incontinence symptoms, which may require additional treatment. Risks associated with all surgical procedures: TVT surgery, like all surgical procedures, carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and anesthesia-related complications.
TVT surgery has been shown to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence in women. Studies have shown that TVT surgery has a success rate of up to 85-90%, and most women experience a significant improvement of their symptoms.
You can try to strengthen the musculature in the pelvic floor yourself through, for example, crunches or Kegel exercises, but it is difficult to achieve a high enough level to make a difference. Some type of customized Yoga training may also be an option depending on what is causing your problem.
With the revolutionary TOP Flat magnetic stimulation technology that Dr. Arnold uses so the researchers have found a solution for effective training of the pelvic floor which drastically reduces and in many cases completely removes the discomfort. Dr. ARNOLD uses a unique magnetic and selective stimulation sequence that interacts with neuromuscular tissues by inducing homogeneous intense muscle contractions (greater than any individual can achieve naturally) without pain or discomfort.
-Don’t let incontinence problems affect your everyday life when a solution is so close at hand. Book a free consultation or directly book a first visit where we do both a consultation, health declaration and investigation as well as an initial treatment.




